To demonstrate our functional lens, we performed four evaluation tests. Spatial resolution or Full width half maximum (FWHM) length Focus shape or Point spread function (PSF) Focal length (f) Image acquired by our microlens Characterization of FWHM, PSF and f
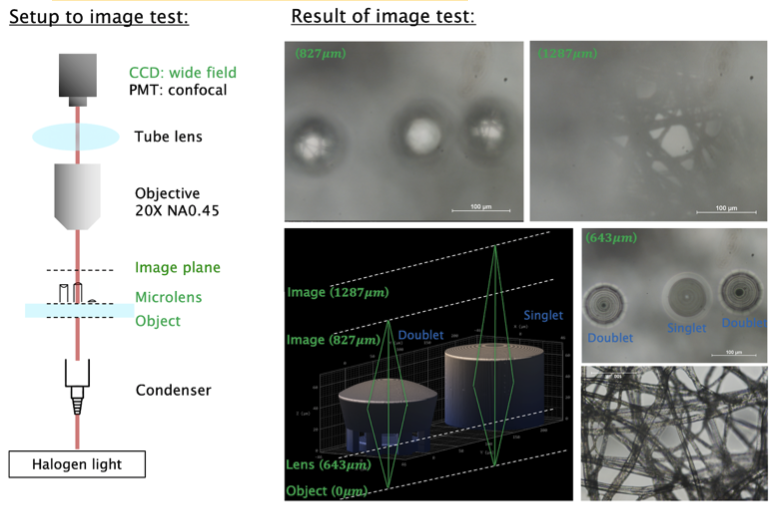
We design an infinite conjugate lens to focus collimated beams into a focus. The setup is shown on the left panel. A supercontinuum laser with AOTF to select 588nm wavelength is fiber coupled and collimated by a biber collimator into free space. This collimated laser beam is focused by microlens and forms a tight focus in a focal plane. The resulting focus is imaged using a high numerical aperture (100x NA = 0.9) objective to microscope system (Nikon Eclipse upright) for either a confocal scanning imaging or wide field CCD image.
The spatial resolution is determined by the full width at half maximum (FWHM) length from Z stack confocal imaging. The resulting FWHM is 0.7 microns which matches with the design 0.69 microns. The focus shape is visualized through PSF. In the confocal image, the PSF is of circular shape, which shows our printed lens is circularly symmetric. We use working distance to compare the focal length between design and the experiment. The working distance is calculated by subtracting the focus Z with the top of the length.
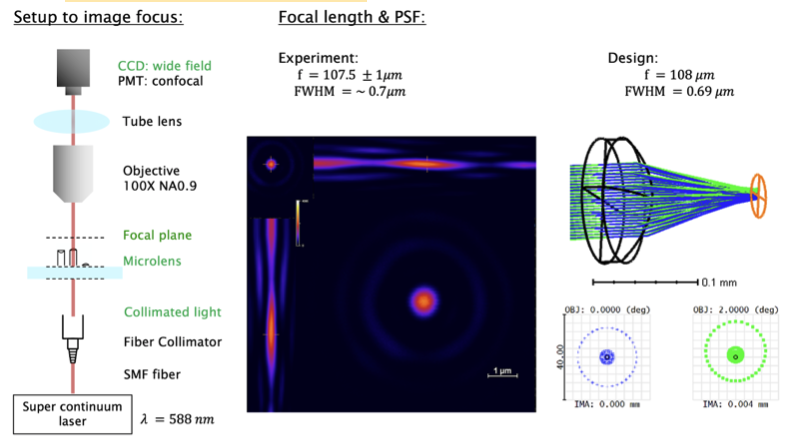
Characterization of image acquired by our microlens
We design a finite conjugate singlet and doublet lens to test the image quality using our printed lens. A tissue sample is used as our test sample. The tissue sample is illuminated by a halogen light source and a condenser. The printed microlens image this tissue sample. The resulting image is imaged using 20x NA 0.45 objective to the microscope system. The image in the inset showed different magnification of the tissue sample from singlet and doublet.